Sino Indian War of 1962
Jawaharlal Nehru
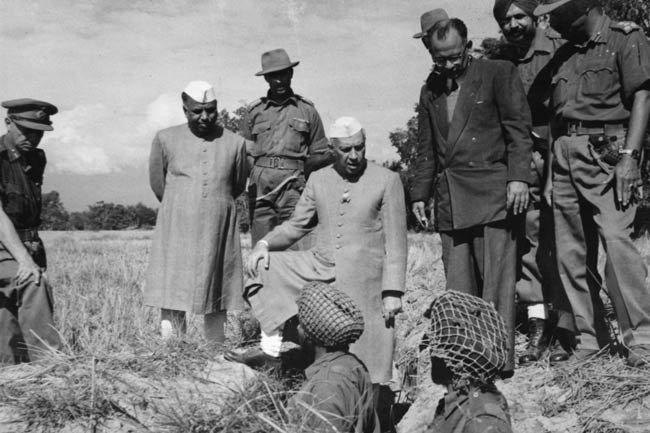

Sino Indian War of 1962
In 1959, Prime Minister Nehru granted asylum to the Dalai Lama and other Tibetan refugees from Chinas 1959 Invasion of Tibet. This sparked tensions between the two Asian superpowers, which already had unsettled claims to the Aksai Chin and Arunachal Pradesh areas in the Himalaya Mountain range. Nehru responded with his Forward Policy, placing military outposts along the disputed border with China, beginning in 1959.On October 20, 1962, China launched a simultaneous attack at two points 1000 kilometers apart along the disputed border with India. Nehru was caught off guard, and India suffered a series of military defeats. By November 21, China felt that it had made its point, and unilaterally ceased fire. It withdrew from its forward positions, leaving the division of land the same as before the war, except that India had been driven from its forward positions across the Line of Control.
Indias force of 10,000 to 12,000 troops suffered heavy losses in the SinoIndian War, with almost 1,400 killed, 1,700 missing, and nearly 4,000 captured by the Peoples Liberation Army of China. China lost 722 killed and about 1,700 wounded. The unexpected war and humiliating defeat profoundly depressed Prime Minister Nehru, and many historians claim that the shock may have hastened his death.
 Nehrus Vision for India
Nehrus Vision for India Education
Education Call for Home Rule
Call for Home Rule Controvery
Controvery Death
Death Nehrus Foreign Policy
Nehrus Foreign Policy Partition and Prime Ministership
Partition and Prime Ministership Nehru as PM
Nehru as PM Early years
Early years Kamala his wife
Kamala his wife Politics and the Independence Struggle
Politics and the Independence Struggle Assessment
Assessment Test your English Language
Test your English Language  Celebration of Nag Panchami
Celebration of Nag Panchami Narendrs Modi
Narendrs Modi Weird Ghost Stories
Weird Ghost Stories Benefits of Pears
Benefits of Pears Precautions while using Shampoo
Precautions while using Shampoo Precautions while using Touch Screen Mobile
Precautions while using Touch Screen Mobile Benefits of Avocado
Benefits of Avocado Benefits of Apples
Benefits of Apples Bollywood Hits
Bollywood Hits




